Discover what Red Eléctrica is, what we do, and why we are the backbone of the electricity system in Spain and the ecological transition.
The demand for electrical energy grows 2.9%
In 2010, the demand for electrical energy on the Spanish peninsula was 259,940 GWh, a 2.9% higher than the figure for 2009 that registered a fall of 4.8% in demand. This gross growth in demand, prior to factoring in the effects of seasonal and working patterns, was 3.2%.
On 19 July two new historical summer records were registered: 41,318 MW of instantaneous power, and an average hourly power of 40,934 MW was reached between 1:00 pm and 2:00 pm.
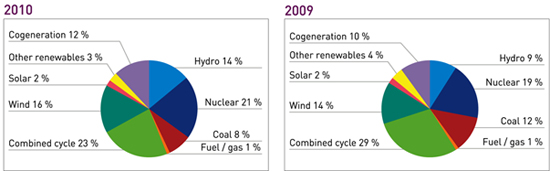
With respect to demand coverage, renewable energies, favoured this year by the high level of reserves of water for hydroelectric power, covered, according to provisional data, 35% of the demand in 2010, six points more than last year.
By technologies, in addition to the indicated growth in hydroelectric generation, noteworthy again is wind power generation which, with a growth of 18.5% in its generation, increased its share of the demand coverage to 16%.
Hydroelectric generation grew 59%
Abundant rainfall registered throughout the majority of 2010, after a period of dry years, has placed producible hydroelectric at 36.568 GWh, the highest since 1997. This value is 30% higher than the historical average value and 65% above the 2009 figure.
Noteworthy therefore in the generation mix figures is the growth of over 59% in hydroelectric generation with respect to the previous year, which has allowed 14% of the 2010 demand to be covered by this technology, compared to 9% in 2009. On the contrary, the coal and combined cycle groups have registered reductions in production of 34% and 17%, respectively, in relation to last year.
The reserves of the reservoirs throughout the peninsula on average are around 65% of their total capacity, the highest value since 1997 and almost 14 points over the reserves registered at the end of 2009.
Wind power production maximums
Wind power energy surpassed, on several occasions, the previous maximums of instantaneous power, hourly energy and daily energy. 9 November registered new historical maximums of wind power production: 14,962 MW of instantaneous power, and 315,258 MWh of daily production, 43% of the electricity demand on that day.
Similarly, in February a monthly maximum of wind power energy was registered which covered 21% of the demand of that month. Nevertheless, the variability which is characteristic of this energy has led to extreme situations such as the one occurred on 9 November when 54% of the demand was covered by this energy at 3:35 am, whereas on 26 June, at 10:32 am, it barely covered 1%.
The increase of renewable energy generation on the one hand, and the lower production from thermal power plants on the other, have contributed to a 20% reduction of CO2 emissions from the electricity sector compared to 2009, estimated at 58.7 million tonnes this year.
Installed power increases by more than 3,700 MW
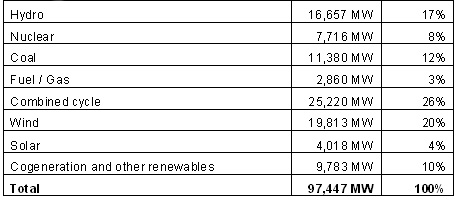
Installed power in generation facilities showed a net growth of 3,717 MW during 2010, reaching a total of 97,447 MW, representing an increase of 4% compared to the previous year.
The majority of this new generation comes from the introduction of 2,154 MW of combined cycle and 1,634 MW of renewable origin facilities, of which 1,094 MW corresponded to wind farms, and 540 MW from solar energy stations. Regarding decommissioning, one fuel-gas generation plant with a power of 148 MW was closed.
Installed power as at 31 December 2010*
* Data relating to the Spanish peninsular system
Extra-peninsular systems
The annual demand for electrical energy in the extra-peninsular systems as a whole fell 1.3% with respect to the previous year. In the Balearic Islands, the fall was 1.7% and in the Canary Islands it was 1.3%. On the contrary, Ceuta and Melilla registered growths of 3.9% and 2.7% respectively.
Export balance on all borders
For the seventh consecutive year, the balance of international exchanges was as an exporter, with 8,490 GWh, 4.8% higher than 2009. This increase is mainly due to the complete change in the net exchange balance with France, which now is of exporter as a result not only of an increase of 45% in exports, but also from a decrease of 49% in imports.
Balance of international exchanges 2010
France -1,387 GWh
Portugal -2,931 GWh
Andorra -270 GWh
Morocco -3,902 GWh
Total -8,490 GWh
NB: Negative figures represent export balances.
Spanish peninsula transmission grid
In 2010 the transmission grid increased by 686.3 km, which means that at the end of the year the Spanish peninsula transmission grid had circuits totalling 35,797 km. Similarly, transformer capacity increased 2,000 MVA.










